
10 Powerful Tips for Efficient Database Management: SQL and NoSQL Integration in Node.js
Streamline your Node.js backend by mastering the integration of SQL and NoSQL databases—these 10 practical tips will help you write cleaner, faster and more scalable data operations.
Dev Orbit
June 24, 2025
Introduction to Database Management
Efficient database management is crucial in today’s data-driven world. As organizations grow and data volume increases, maintaining performance, scalability and reliability becomes essential. Database management systems (DBMS) are software applications that interact with databases, providing users with tools to create, retrieve, update and manage data.
What is SQL?
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a standard programming language specifically designed for managing and manipulating relational databases. SQL databases are known for their ability to handle complex queries, support ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) properties and provide robust transactional support.
Key Features of SQL
Structured Data: SQL databases are based on a fixed schema, making them ideal for structured data.
ACID Compliance: Ensures reliable transactions and data integrity.
Complex Queries: SQL supports complex joins and subqueries.
Examples of SQL Databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, Oracle Database.
What is NoSQL?
NoSQL (Not Only SQL) databases are designed to handle unstructured or semi-structured data. They offer flexible schema design and horizontal scalability, making them suitable for large-scale and real-time applications.
Key Features of NoSQL
Schema Flexibility: NoSQL databases can store different types of data without a predefined schema.
Scalability: Designed to scale out horizontally across multiple servers.
Variety of Data Models: Includes document-based, key-value, column-family and graph databases.
Examples of NoSQL Databases: MongoDB, CouchDB, Redis, Cassandra.
SQL vs NoSQL
Understanding the differences between SQL and NoSQL is essential for choosing the right database for your application.
Differences
Data Structure: SQL uses a structured schema, while NoSQL offers schema-less design.
Scalability: SQL scales vertically, NoSQL scales horizontally.
Transactions: SQL supports complex transactions, NoSQL offers eventual consistency.
Use Cases
SQL: Suitable for transactional systems accounting software and applications requiring complex queries.
NoSQL: Ideal for real-time analytics, content management systems and applications with rapidly changing data.
Pros and Cons
SQL Pros: ACID compliance, complex query support, mature ecosystem.
SQL Cons: Limited horizontal scalability, rigid schema.
NoSQL Pros: Flexible schema, horizontal scalability, high performance for specific workloads.
NoSQL Cons: Limited support for complex queries, eventual consistency model.
Introduction to Node.js
Node.js is a powerful, event-driven JavaScript runtime built on Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine. It allows developers to build scalable network applications with ease, offering non-blocking I/O and a single-threaded event loop architecture.
Benefits of Using Node.js for Database Management
Asynchronous Processing: Handles multiple operations concurrently, enhancing performance.
Scalability: Suitable for building high-performance, scalable applications.
Community Support: Extensive libraries and frameworks available through npm (Node Package Manager).
Setting Up Node.js for Database Integration Installation
Download Node.js: Visit the official Node.js website and download the latest version.
Install Node.js: Follow the installation instructions for your operating system.
Verify Installation: Open a terminal and run
node -vto check the Node.js version.
Basic Configuration
Create a Project Directory: Run
mkdir my-node-appand navigate into the directory.Initialize Project: Run
npm initto create apackage.jsonfile.
Required Packages
Express.js: For building web applications and APIs.
npm install expressDatabase Drivers: Install specific drivers for your chosen database (e.g., mysql, pg, mongodb).
Integrating SQL Databases in Node.js
Popular SQL Databases for Node.js
MySQL: Widely used open-source relational database.
PostgreSQL: Advanced open-source relational database with powerful features.
SQLite: Lightweight, file-based relational database.
Installing and Configuring SQL Databases
MySQL :
npm install mysqlPostgreSQL :
npm install pgSQLite :
npm install sqlite3
Working with MySQL in Node.js
Installation
Install MySQL: Follow instructions for your operating system.
Install Node.js Driver:
npm install mysql.
Configuration
Create a MySQL Database: Use MySQL Workbench or command line.
Connect to MySQL in Node.js:
const mysql = require('mysql');
const connection = mysql.createConnection({
host: 'localhost',
user: 'root',
password: '',
database: 'mydb'
});
connection.connect();CRUD Operations
// Create
connection.query('INSERT INTO users SET ?', {name: 'John Doe'}, (error, results) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('User added:', results.insertId);
});
// Read
connection.query('SELECT * FROM users', (error, results) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('Users:', results);
});
// Update
connection.query('UPDATE users SET name = ? WHERE id = ?', ['Jane Doe', 1], (error, results) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('User updated:', results.message);
});
// Delete
connection.query('DELETE FROM users WHERE id = ?', [1], (error, results) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('User deleted:', results.affectedRows);
});Working with PostgreSQL in Node.js Installation
Install PostgreSQL: Follow instructions for your operating system.
Install Node.js Driver:
npm install pg.
Configuration
Create a PostgreSQL Database: Use pgAdmin or command line.
Connect to PostgreSQL in Node.js:
const { Client } = require('pg');
const client = new Client({
user: 'postgres',
host: 'localhost',
database: 'mydb',
password: '',
port: 5432,
});
client.connect();CRUD Operations
// Create
client.query('INSERT INTO users(name) VALUES($1) RETURNING id', ['John Doe'], (error, results) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('User added:', results.rows[0].id);
});
// Read
client.query('SELECT * FROM users', (error, results) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('Users:', results.rows);
});
// Update
client.query('UPDATE users SET name = $1 WHERE id = $2', ['Jane Doe', 1], (error, results) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('User updated:', results.rowCount);
});
// Delete
client.query('DELETE FROM users WHERE id = $1', [1], (error, results) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('User deleted:', results.rowCount);
});Working with SQLite in Node.js
Installation
Install SQLite: Follow instructions for your operating system.
Install Node.js Driver:
npm install sqlite3.
Configuration
Connect to SQLite in Node.js:
const sqlite3 = require('sqlite3').verbose();
const db = new sqlite3.Database(':memory:');CRUD Operations
// Create
db.run('CREATE TABLE users (id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, name TEXT)', (error) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('Table created');
});
// Read
db.all('SELECT * FROM users', (error, rows) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('Users:', rows);
});
// Update
db.run('UPDATE users SET name = ? WHERE id = ?', ['Jane Doe', 1], (error) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('User updated');
});
// Delete
db.run('DELETE FROM users WHERE id = ?', [1], (error) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('User deleted');
});Integrating NoSQL Databases in Node.js
Popular NoSQL Databases for Node.js
MongoDB: Document-oriented NoSQL database.
CouchDB: Schema-free document-oriented database.
Redis: In-memory key-value store.
Installing and Configuring NoSQL Databases
MongoDB :
npm install mongodbCouchDB :
npm install nanoRedis :
npm install redis
Working with MongoDB in Node.js
Installation
Install MongoDB: Follow instructions for your operating system.
Install Node.js Driver:
npm install mongodb.
Configuration
Create a MongoDB Database: Use MongoDB Compass or command line.
Connect to MongoDB in Node.js:
const { MongoClient } = require('mongodb');
const client = new MongoClient('mongodb://localhost:27017');
client.connect();
const db = client.db('mydb');CRUD Operations
// Create
db.collection('users').insertOne({name: 'John Doe'}, (error, result) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('User added:', result.insertedId);
});
// Read
db.collection('users').find().toArray((error, users) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('Users:', users);
});
// Update
db.collection('users').updateOne({id: 1}, {$set: {name: 'Jane Doe'}}, (error, result) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('User updated:', result.modifiedCount);
});
// Delete
db.collection('users').deleteOne({id: 1}, (error, result) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('User deleted:', result.deletedCount);
});Working with CouchDB in Node.js
Installation
Install CouchDB: Follow instructions for your operating system.
Install Node.js Driver:
npm install nano.
Configuration
Create a CouchDB Database: Use Fauxton or command line.
Connect to CouchDB in Node.js:
const nano = require('nano')('http://localhost:5984');
const db = nano.db.use('mydb');CRUD Operations
// Create
db.insert({name: 'John Doe'}, (error, body) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('User added:', body.id);
});
// Read
db.list({include_docs: true}, (error, body) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('Users:', body.rows);
});
// Delete
db.destroy('user_1', '1-xxx', (error, body) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('User deleted:', body.id);
});
// Update
db.insert({_id: 'user_1', _rev: '1-xxx', name: 'Jane Doe'}, (error, body) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('User updated:', body.id);
});Working with Redis in Node.js
Installation
Install Redis: Follow instructions for your operating system.
Install Node.js Driver:
npm install redis.
Configuration
Connect to Redis in Node.js:
const redis = require('redis');
const client = redis.createClient();
client.on('connect', () => {
console.log('Connected to Redis');
});CRUD Operations
// Create
client.set('user:1', JSON.stringify({name: 'John Doe'}), (error, reply) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('User added:', reply);
});
// Read
client.get('user:1', (error, reply) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('User:', JSON.parse(reply));
});
// Update
client.set('user:1', JSON.stringify({name: 'Jane Doe'}), (error, reply) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('User updated:', reply);
});
// Delete
client.del('user:1', (error, reply) => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log('User deleted:', reply);
});Choosing the Right Database for Your Node.js Application
Factors to Consider
Data Structure: Choose SQL for structured data, NoSQL for unstructured or semi-structured data.
Scalability: Consider the scalability requirements of your application.
Query Complexity: Use SQL for complex queries and transactions, NoSQL for simple queries and large-scale data.
Performance
SQL: Best for read-heavy workloads.
NoSQL: Suitable for write-heavy and real-time applications.
Scalability
SQL: Vertical scaling (adding more resources to a single server).
NoSQL: Horizontal scaling (adding more servers).
Combining SQL and NoSQL in Node.js Applications
Use Cases
Hybrid Applications: Applications requiring both structured and unstructured data.
Polyglot Persistence: Using multiple databases for different types of data within the same application.
Benefits
Flexibility: Leverage the strengths of both SQL and NoSQL.
Performance: Optimize data storage and retrieval for different types of data.
Challenges
Complexity: Managing multiple database systems can be complex.
Consistency: Ensuring data consistency across different databases.
Data Modeling for SQL and NoSQL Integration
Strategies
Unified Data Model: Design a data model that can work with both SQL and NoSQL databases.
Separate Models: Use different data models for different databases based on data type and access patterns.
Best Practices
Data Normalization: Normalize data in SQL databases.
Data Denormalization: Denormalize data in NoSQL databases for performance.
Tools
ORM (Object-Relational Mapping): Use ORMs like Sequelize for SQL databases.
ODM (Object-Document Mapping): Use ODMs like Mongoose for NoSQL databases.
Handling Transactions in SQL and NoSQL Databases
Concepts
ACID Transactions: Ensure atomicity, consistency, isolation and durability in SQL databases.
BASE Transactions: Ensure basic availability, soft state and eventual consistency in NoSQL databases.
Implementation in Node.js
SQL Transactions:
connection.beginTransaction((err) => {
if (err) throw err;
connection.query('INSERT INTO users SET ?', {name: 'John Doe'}, (err, result) => {
if (err) {
return connection.rollback(() => {
throw err;
});
}
connection.commit((err) => {
if (err) {
return connection.rollback(() => {
throw err;
});
}
console.log('Transaction complete.');
});
});
});NoSQL Transactions:
db.collection('users').insertOne({name: 'John Doe'}, {session}, (error, result) => {
if (error) {
session.abortTransaction();
throw error;
}
session.commitTransaction();
console.log('Transaction complete.');
});Data Migration Between SQL and NoSQL
Tools and Techniques
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load): Use ETL tools to migrate data between SQL and NoSQL databases.
Data Pipelines: Create data pipelines for continuous data migration.
Best Practices
Plan Migration: Thoroughly plan the migration process.
Test Migration: Perform test migrations to ensure data integrity.
Monitor Migration: Monitor the migration process to address issues promptly.
Ensuring Data Consistency and Integrity
Techniques
Use Transactions: Ensure data consistency with transactions.
Data Validation: Validate data before inserting it into the database.
Tools
Database Constraints: Use constraints to enforce data integrity in SQL databases.
Validation Libraries: Use libraries like Joi for data validation in Node.js.
Best Practices
Regular Audits: Regularly audit databases to ensure data integrity.
Automated Testing: Implement automated tests to check for data consistency.
Optimizing Database Performance in Node.js
Tips and Tricks
Indexing: Use indexing to speed up data retrieval.
Caching: Implement caching to reduce database load.
Tools
Monitoring Tools: Use tools like PM2 and New Relic to monitor performance.
Profiling Tools: Use profiling tools to identify bottlenecks.
Monitoring Performance
Regular Monitoring: Continuously monitor database performance.
Performance Tuning: Regularly tune the database to maintain optimal performance.
Security Considerations for Database Management in Node.js
Best Practices
Use Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data.
Access Control: Implement strict access control policies.
Regular Updates: Keep database and Node.js packages up to date.
Common Vulnerabilities
SQL Injection: Prevent SQL injection attacks by using parameterized queries.
NoSQL Injection: Use validation to prevent NoSQL injection attacks.
Tools
Security Tools: Use tools like OWASP ZAP to scan for vulnerabilities.
Libraries: Use libraries like Helmet to enhance security in Node.js applications.
Backup and Recovery Strategies
Importance
Data Loss Prevention: Protect against data loss.
Disaster Recovery: Ensure business continuity in case of a disaster.
Tools
Backup Tools: Use tools like mysqldump for SQL databases and mongodump for MongoDB.
Recovery Tools: Ensure you have the necessary tools to recover data from backups.
Best Practices
Regular Backups: Schedule regular backups.
Test Backups: Regularly test backups to ensure they can be restored.
Real-World Applications of SQL and NoSQL Integration in Node.js
Case Studies
E-commerce Platforms: Combining SQL for transactions and NoSQL for product catalogs.
Social Media Applications: Using SQL for user data and NoSQL for activity feeds.
Examples
Hybrid Systems: Systems that leverage both SQL and NoSQL databases for optimal performance and flexibility.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Database Management
Common Problems
Connection Issues: Problems with connecting to the database.
Query Performance: Slow query performance.
Data Inconsistency: Issues with data consistency.
Solutions
Check Configuration: Ensure database configuration is correct.
Optimize Queries: Use query optimization techniques.
Regular Audits: Perform regular audits to identify and fix data inconsistencies.
Tips
Stay Updated: Keep database systems and drivers up to date.
Use Logging: Implement logging to track and troubleshoot issues.
Future Trends in Database Management
Emerging Technologies
Distributed Databases: Rise of distributed databases for high availability.
AI and ML Integration: Use of AI and ML to enhance database management.
Predictions
Increased Automation: More automation in database management tasks.
Enhanced Security: Stronger focus on database security.
Innovations
New Database Models: Development of new database models to meet evolving needs.
Performance Enhancements: Continued improvements in database performance.
Community and Resources
Forums
Stack Overflow: Community support for database management in Node.js.
Reddit: Subreddits dedicated to Node.js and database management.
Tutorials
MDN Web Docs: Comprehensive tutorials on using databases with Node.js.
YouTube: Video tutorials on database integration in Node.js.
Documentation
Official Docs: Documentation for Node.js, MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, etc.
API References: API references for database drivers and libraries.
Tools
npm: Node Package Manager for finding and installing packages.
GitHub: Source code repositories for open-source projects.
Conclusion
Efficient database management with SQL and NoSQL integration in Node.js offers a powerful approach to handling diverse data needs. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each database type, you can make informed decisions and build scalable, high-performance applications. Embrace the future of database management with a hybrid approach and stay ahead of the curve with continuous learning and adaptation.
FAQs
Q: What are the main differences between SQL and NoSQL databases?
Ans: SQL databases use a structured schema and support complex queries, while NoSQL databases offer flexible schema design and horizontal scalability.
Q: Why should I use Node.js for database management?
Ans: Node.js provides asynchronous processing, scalability and a rich ecosystem of libraries, making it ideal for database management.
Q: How do I choose between SQL and NoSQL for my application?
Ans: Consider factors like data structure, scalability requirements and query complexity. SQL is suited for structured data and complex queries, while NoSQL is ideal for unstructured data and high scalability.
Q: Can I use both SQL and NoSQL in a single application?
Ans: Yes, using both types of databases in a single application is known as polyglot persistence and allows you to leverage the strengths of each database type.
Q: What are some popular SQL and NoSQL databases for Node.js?
Ans: Popular SQL databases include MySQL, PostgreSQL and SQLite. Popular NoSQL databases include MongoDB, CouchDB and Redis.
Q: How can I ensure data consistency when using multiple databases?
Ans: Use transactions, data validation and regular audits to ensure data consistency across different databases.

Enjoyed this article?
Subscribe to our newsletter and never miss out on new articles and updates.
More from Dev Orbit

GitHub Copilot vs Tabnine (2025): Which AI Assistant is Best?
AI coding assistants are no longer futuristic experiments—they’re becoming essential tools in the modern developer’s workflow. In this review, we’ll compare GitHub Copilot and Tabnine head-to-head in 2025, exploring how each performs in real-world backend coding tasks. From productivity gains to code quality, we’ll answer the burning question: Which AI assistant should you trust with your code?
Top AI Tools to Skyrocket Your Team’s Productivity in 2025
As we embrace a new era of technology, the reliance on Artificial Intelligence (AI) is becoming paramount for teams aiming for high productivity. This blog will dive into the top-tier AI tools anticipated for 2025, empowering your team to automate mundane tasks, streamline workflows, and unleash their creativity. Read on to discover how these innovations can revolutionize your workplace and maximize efficiency.

NestJS Knex Example: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Scalable SQL Application
Are you trying to use Knex.js with NestJS but feeling lost? You're not alone. While NestJS is packed with modern features, integrating it with SQL query builders like Knex requires a bit of setup. This beginner-friendly guide walks you through how to connect Knex with NestJS from scratch, covering configuration, migrations, query examples, real-world use cases and best practices. Whether you're using PostgreSQL, MySQL or SQLite, this comprehensive tutorial will help you build powerful and scalable SQL-based applications using Knex and NestJS.

Unlocking WASI: The Future of Serverless with WebAssembly
Discover how WASI is transforming serverless computing with secure, portable WebAssembly runtimes for the cloud era.

Handling File Uploads Using Multer In Node Js Express
Web developers must understand how to handle file uploads in the fast-changing world of web development. Multer in Node.js is a robust solution for this task. This article explores Multer features, installation process, advanced functionalities and best practices for seamless integration with Express.

Avoid These Common Node.js Backend Development Mistakes
Introduce the significance of Node.js in backend development and how its popularity has led to an array of common mistakes that developers might overlook.
Releted Blogs
Spotify Wrapped Is Everything Wrong With The Music Industry
Every year, millions of Spotify users eagerly anticipate their Spotify Wrapped, revealing their most-listened-to songs, artists and genres. While this personalized year-in-review feature garners excitement, it also highlights critical flaws in the contemporary music industry. In this article, we explore how Spotify Wrapped serves as a microcosm of larger issues affecting artists, listeners and the industry's overall ecosystem.

From Autocompletion to Agentic Reasoning: The Evolution of AI Code Assistants
Discover how AI code assistants have progressed from simple autocompletion tools to highly sophisticated systems capable of agentic reasoning. This article explores the innovations driving this transformation and what it means for developers and technical teams alike.

Data Validation in Machine Learning Pipelines: Catching Bad Data Before It Breaks Your Model
In the rapidly evolving landscape of machine learning, ensuring data quality is paramount. Data validation acts as a safeguard, helping data scientists and engineers catch errors before they compromise model performance. This article delves into the importance of data validation, various techniques to implement it, and best practices for creating robust machine learning pipelines. We will explore real-world case studies, industry trends, and practical advice to enhance your understanding and implementation of data validation.
Why Most People Waste Their AI Prompts ? How to Fix It...
In the current landscape of AI technology, many users struggle with crafting effective prompts. This article explores common pitfalls and offers actionable strategies to unlock the true potential of AI tools like GPT-5.

Deep Dive into Error Handling and Logging in Node.js
Mastering the essentials of error handling and logging in Node.js for more resilient backends.
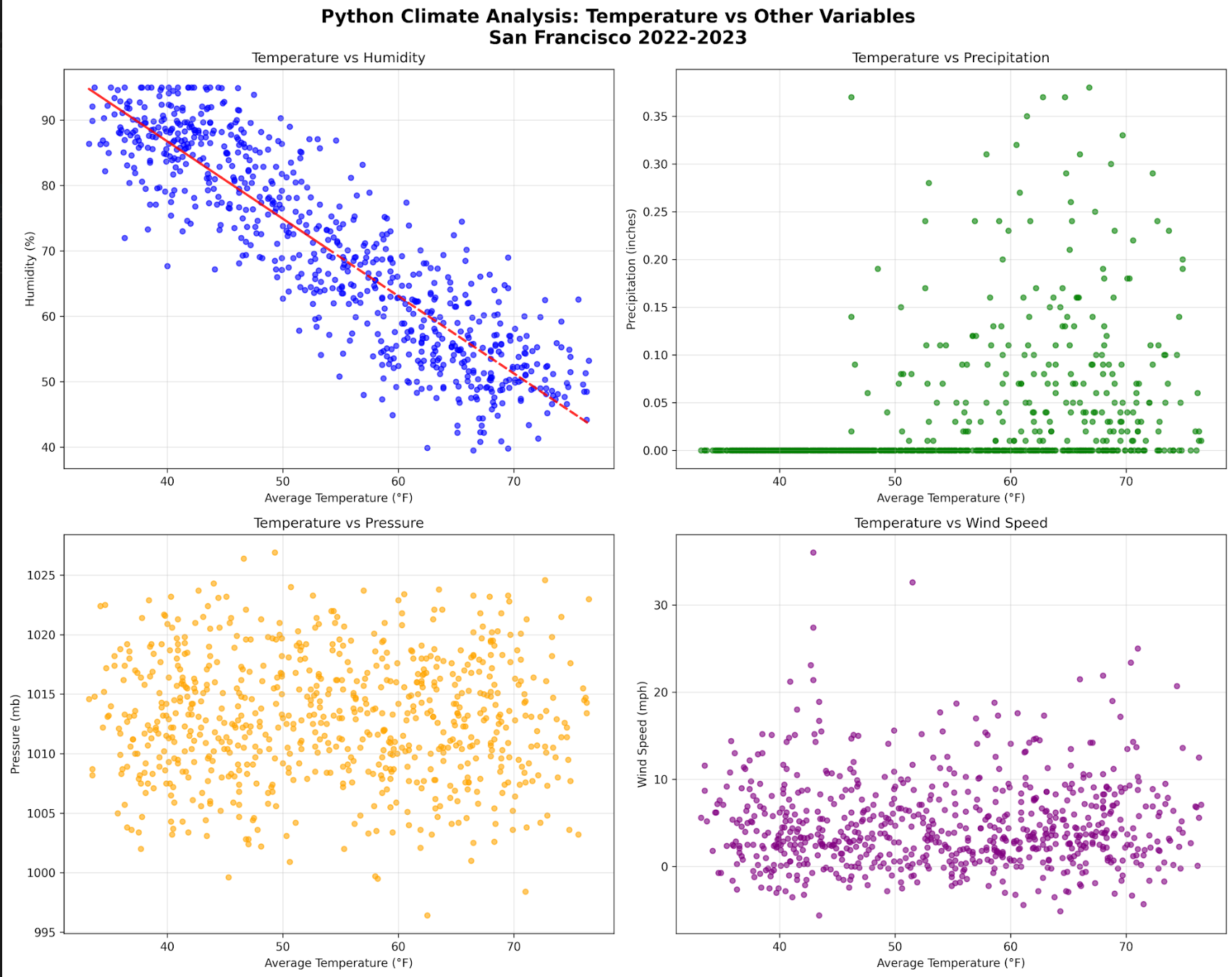
Python vs R vs SQL: Choosing Your Climate Data Stack
Delve into the intricacies of data analysis within climate science by exploring the comparative strengths of Python, R and SQL. This article will guide you through selecting the right tools for your climate data needs, ensuring efficient handling of complex datasets.
Have a story to tell?
Join our community of writers and share your insights with the world.
Start Writing